Filamentous microfossils in a 3,235-million-year-old volcanogenic massive sulphide deposit
BIRGER RASMUSSEN
Department of Geology and Geophysics, University of Western Australia , Nedlands, Western Australia 6907, Australia
The record of Archaean microfossils is sparse[1]. Of the few bona fide fossil assemblages, most are from shallow-water settings, and they are typically associated with laminated, stromatolitic sedimentary rocks[2-4]. Microfossils from deep-sea hydrothermal systems have not been reported in Precambrian rocks (> 544 million years old), although thermophilic microbes are ubiquitous in modern sea-floor hydrothermal settings[5, 6], and apparently have the most ancient lineages[7, 8]. Here, I report the discovery of pyritic filaments, the probable fossil remains of thread-like microorganisms, in a 3,235-million-year-old deep-sea volcanogenic massive sulphide deposit from the Pilbara Craton of Australia. From their mode of occurrence, the micro-organisms were probably thermophilic chemotropic prokaryotes, which inhabited sub-sea-floor hydrothermal environments. They represent the first fossil evidence for microbial life in a Precambrian submarine thermal spring system, and extend the known range of submarine hydrothermal biota by more than 2,700 million years[9]. Such environments may have hosted the first living systems on Earth, consistent with proposals for a thermophilic origin of life[10-13].
The Pilbara Craton of Australia contains one of the most complete sections of well preserved Archaean volcano-sedimentary rocks and is the site of several previous fossil discoveries[4, 14]. From this region, the probable fossil remains of microorganisms were identified in a volcanogenic massive sulphide (VMS) deposit at Sulphur Springs. The deposit is located in low-strain, very low metamorphic grade (prehnite–pumpellyite facies) rocks of the northern Soanesville belt in the eastern Pilbara Craton (Fig. 1a), and displays exceptional textural and structural preservation despite its great age[15]. Mineralization is associated with syn-volcanic faults and lies below a regionally extensive unit of silicified sedimentary and volcaniclastic rocks ('marker chert') which caps a succession of mafic, intermediate and felsic volcanic rocks and syn-volcanic dacitic intrusions (Fig. 1b). These rocks are intruded by the 3,235-Myr-old co-magmatic Strelley granite, which is synchronous with hydrothermal mineralization[16-18]. The succession was deposited in a deep marine setting, with water depths probably exceeding 1,000 m, as indicated by volcanic textures, sedimentary facies and style of metal precipitation[15, 16].
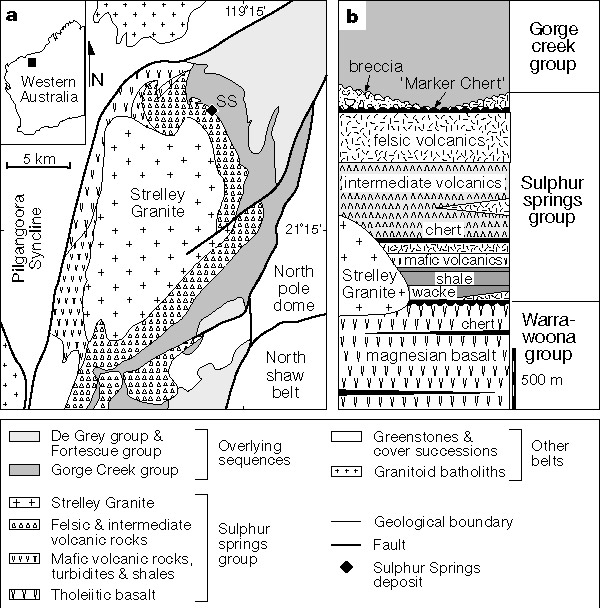
Figure 1 Location and geology of the Sulphur Springs deposit. a, Map showing the geology of the northern Soanesville belt and the location of the Sulphur Springs deposit (after ref. 16). b, Stratigraphic column of the Sulphur Springs group (after ref. 18).
The deposit (UTM grid 728976594) consists of stratabound lenses of pyrite, sphalerite, chalcopyrite, tennantite, galena, barite and quartz, and an underlying stringer zone with veins of quartz, pyrite, chalcopyrite, and minor sphalerite and carbonate. The lower part is characterized by massive, granular, honeycomb and filigree sulphide textures, whereas the upper part contains dendritic, colloform and pellet textures[15]. Bitumen occurs in small quantities throughout the deposit as blocky fragments and films that are intergrown with sulphides, and oil is present as fluid inclusions in hydrothermal barite[19]. The deposit displays an upward and outward zonation from Cu to Zn–Pb, a diagnostic feature of VMS-style mineralization. Galena from the deposit gives a Pb–Pb model age of 3,260 Myr (ref. 15). The composition of the ore indicates that fluid temperatures probably reached 300 °C (ref. 15), but distal areas were probably much cooler. Much of the mineralization formed by replacement of volcanic and volcaniclastic rocks close to the sea floor16, although it has been argued that open-space sulphide textures indicate a setting resembling black-smoker chimneys at hydrothermal vents[15].
Polished thin sections from the deposit were examined by optical microscopy (using transmitted and reflected light) and scanning electron microscopy. Filaments are located in the siliceous cores and bands of colloform structures (Fig. 2a, b) from samples in the upper part of the deposit. These rocks consist of pyrite and microcrystalline quartz (chert), with minor sphalerite, chalcopyrite, tennantite, arsenopyrite, galena, chlorite and carbonate, and up to 10% of silicified volcanic rock fragments. The colloform structures range in size from <0.1 mm to several centimetres, and include botryoidal, coalesced and branching forms. The structures are almost entirely composed of inclusion-rich pyrite, and are enclosed by paragenetically late chert. Much of the pyrite has been recrystallized to massive pyrite by the influx of late-stage hydrothermal fluids, and many of the structures show evidence of progressive replacement by later sulphides.
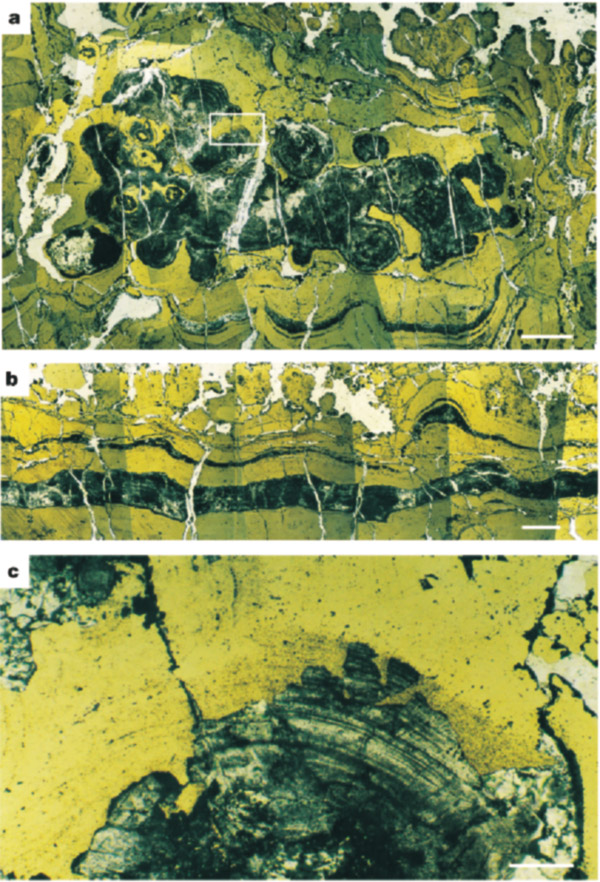
Figure 2 Remnant cores and bands containing filaments. a, Silica-rich colloform cores containing filaments, surrounded by replacive pyrite (gold). Combined transmitted and reflected light (TL and RL) photographic montage. b, Thin banded layer containing filaments within paragenetically early chert (TL and RL). c, Detail of a showing the partial replacement of quartz-rich colloform structures displaying fine-scale lamination (TL and RL). Scale bar is 1 mm for a, b and 0.1 mm for c.
The banding and concentric textures preserved in many colloform structures are defined by inclusions after the incomplete replacement of original minerals by pyrite (Fig. 2c). In the few samples where original minerals are preserved, they comprise inclusion-rich chert, coarse quartz crystals and rare carbonate rhombs. Although most of the microcrystalline silica has been recrystallized to coarser quartz, some fine morphological detail is preserved as banding. Individual laminae are typically 5–50 µm thick, and are defined by alternating light and dark zones and by trails of irregular pyrite crystals that extend across interlocking quartz crystals. The colloform cores also contain later infilling aggregates of siderite, inclusion-free quartz and chlorite. The colloform structures are cut by fibrous quartz veins that also contain minor chlorite, carbonate, sphalerite and pyrite, which extend up to a few millimetres into the surrounding pyrite ( Fig. 2a).
The filaments are located in the paragenetically early chert and coarse-grained quartz, and are absent in later generation silica, carbonate, chlorite and sulphide. The filaments are threadlike, unbranched and of uniform thickness along their length (0.5–2 µm in diameter, up to 300 µm long). They include straight, sinuous and sharply curved morphologies which are intertwined where they are densely distributed (Fig. 3a–f ). They are abundant, with over 300 filaments in a 5 mm 10 mm area in one polished thin section (30 µm thick). In reflected light, the filaments appear to be almost entirely composed of many sub-micrometre-sized pyrite crystals. In the cores of colloform structures, most filaments appear to be randomly oriented, but towards the outer margins they are aligned parallel to concentric layering (Fig. 3g) or, less commonly, are oriented sub-perpendicular to the banding ( Figs 3h, 4). In some bands (<1 mm to 20 mm long) most filaments lie parallel to lamination ( Fig. 4). The filaments extend across the interlocking crystal boundaries of early chert, coarse quartz and carbonate rhombs, and in places are disrupted and displaced by silica-filled penetrative fractures (Fig. 3f).
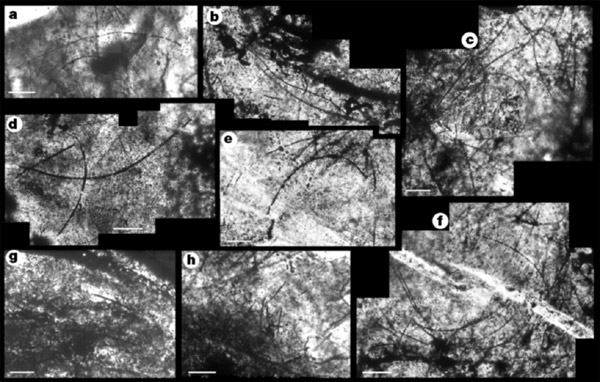
Figure 3 Photomicrographs of filaments from the Sulphur Springs VMS deposit. Scale bar, 10 µm. a–f, Straight, sinuous and curved morphologies, some densely intertwined. g, Filaments parallel to the concentric layering. h, Filaments oriented sub-perpendicular to banding.
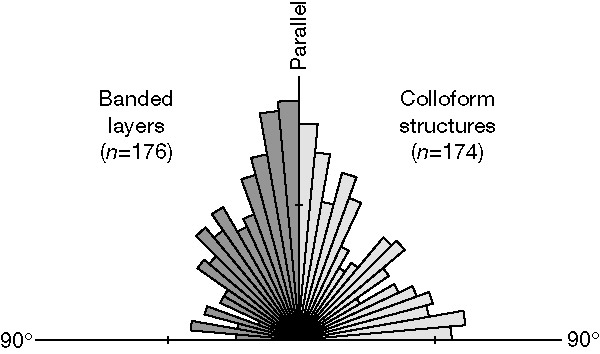
Figure 4 Rose diagram showing filament orientation relative to lamination for colloform structures and banded layers using 5° subdivisions.
The filaments can be traced through different focal levels within thin sections, and are present in several thin sections of the same sample and in many samples from various parts of the deposit. Because the samples are from subsurface (300–350 m) diamond drill-core, well below the water table and with no evidence of weathering, emplacement by modern surface fluids can be dismissed. Thus, the filaments are indigenous to the host rocks. The presence of filaments within paragenetically early minerals which are almost completely replaced by later sulphides and their disruption by cross-cutting fractures indicates that they are syngenetic and were lithified before the main stage of sulphide mineralization, coincident with granitoid intrusion 3,235 Myr ago[18].
A biogenic origin is inferred for the filaments from their sinuous morphology, length-wise uniformity and intertwined habit, which are comparable to those of Archaean and younger microfossils[1-4, 20]. They are entirely dissimilar to abiogenic filamentous microstructures formed by the displacement of carbonaceous matter during crystal growth or the movement of ambient pyrite crystals[21, 22]. The limited range of morphotypes may reflect selective diagenetic preservation[23] or low initial diversity. Perhaps most significantly, the changes in preferred orientation of filaments in different areas of the colloform structures may indicate behavioural variations in different micro-environments, a distinctly biological feature. Similar patterns are evident in modern microbial mats[24] and hot-spring communities[25], indicating a biotic tropism or taxis in response to a gradient or fluctuation in a salient ecological parameter. It therefore seems reasonable to infer that the Sulphur Springs filaments are probably biogenic, and as such, represent the best available evidence for microbial life in a hydrothermal setting during the Precambrian.
Although it is difficult to ascribe metabolic characteristics to fossilized microbes on the basis of morphology[1, 2], some information can be inferred from their mode of occurrence. In the Sulphur Springs deposit, the presence of volcanic rock fragments in many of the fossiliferous samples and their location below a silicified cap of sedimentary and volcaniclastic rocks indicate that the microorganisms probably lived in the pores and crevices of rocks at shallow depths below the sea floor. In such a setting, proximal hydrothermal fluids would have delivered a near-continuous supply of nutrients and metals essential for growth[12]. The filaments, which probably acted as nucleation sites[25, 26], were consequently engulfed by paragenetically early silica, which precipitated as mineral-charged hydrothermal fluids cooled upon approaching the sea floor. As the hydrothermal system evolved, with the formation of hotter fluids owing to the emplacement of the Strelley Granite, the early, low-temperature silica was progressively replaced by pyrite and later sulphides. Although there were several episodes of silicification, with resultant cementation of pores and replacement of precursor sedimentary and volcaniclastic rocks, it is unclear whether the early silica was generated during volcanism, syn-volcanic intrusion or the earliest stage of granite intrusion.
Given that the filamentous microfossils are encased in hydrothermal silica, and are within a VMS deposit, it seems likely that the microbiota were thermophiles, inhabiting 'low-temperature' (<110 °C) sub-sea-floor niches adjacent to discharging hydrothermal fluids. The oil in the deposit[19] indicates that hydrocarbons entrained by circulating fluids may have provided readily bioavailable energy and carbon sources for microorganisms living around the hydrothermal system[6, 27, 28]. The great water depth (>1,000 m) and sediment cover would have offered protection from ultraviolet radiation, and imply that the filamentous microbiota could not have derived energy for growth through light-dependent processes; instead they must have used chemical pathways for metabolic processes. The abundance of reduced chemical species in sea-floor hydrothermal fluids and the probable absence of dissolved oxygen in the Archaean deep ocean[29] indicates that these pathways were probably anaerobic. As in modern deep-sea hydrothermal systems[5, 6], the abundance of reduced sulphur in the hydrothermal fluids and the encrustation of filaments by pyrite indicate that sulphur may have been central to energy-yielding reactions for microbial growth.